Larval Development of Helminths Occurs in Which Host
Other worms have larvae that actively penetrate the skin hookworms schistosomes Strongyloides. Larvae and eggs are developmental forms of.
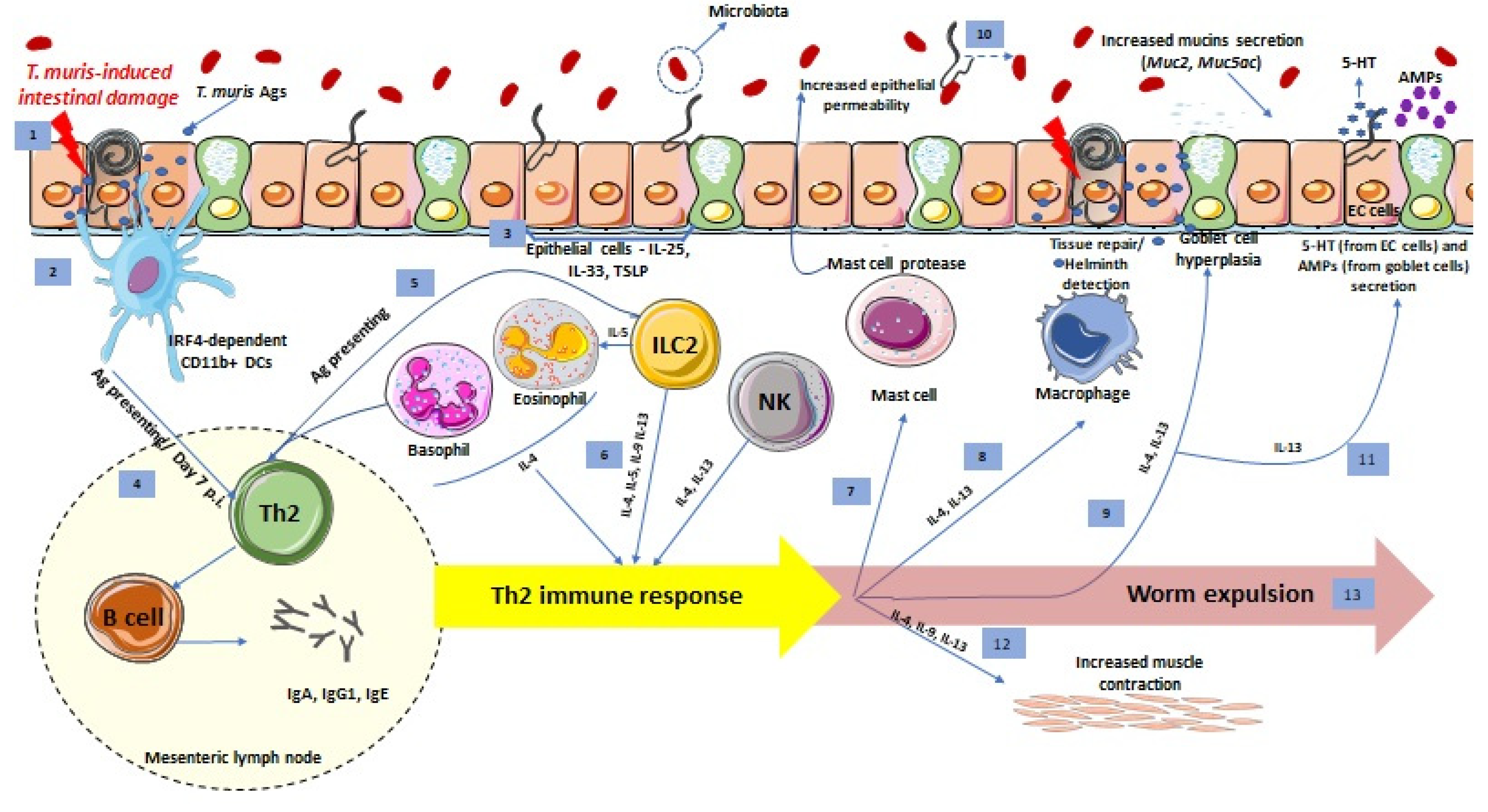
Pathogens Free Full Text Trichuris Muris Model Role In Understanding Intestinal Immune Response Inflammation And Host Defense Html
Figure 1 Helminth-induced pathogenesis of human pulmonary disease.

. Are identified in the laboratory by microscopic examination of body fluids and excretions containing the eggs and larvae. When a eukaryotic cell is not undergoing mitosis the DNA and its associated proteins appear as a visible network of dark fibers called the. In several cases infection requires an intermediate host vector.
Known as athletes foot Cilia are structures for motility found primarily in. Larval development of helminths occurs in which host. Find read and cite all the research you need.
Paratenic host is more an ecological than a physiological phenomenon in the transmission of helminths. Mating occurs in all hosts. The simplest is by accidental ingestion of infective eggs Ascaris Echinococcus Enterobius Trichuris or larvae some hookworms.
A Primary host B Intermediate host C Definitive host D Transport host E Larvaldevelopment takes. Elgar in Encyclopedia of Animal Behavior Second Edition 2019 Host-marking. Hatched helminth larvae transform through various larval stages in the trematodes and cestodes or mature through a series of four molts in the nematodes.
The eggs of the parasitoid hatch and the larvae commence eating the inside of their host which eventually dies as the parasitoid pupates. A second major question concerns why trophically transmitted larval helminths appear ubiquitously to avoid the gut of the intermediate host and migrate to. The factors that influence the development survival distribution or migratory behavior of the free-living larvae seen on pasture are primarily weather related.
The larvae may live for several weeks on the soil. Because host condition age size sex can influence the growth of larval helminths in their intermediate host Parker et al 2003b we used only male. Egg hatching is triggered by altera- tions in the external environment and effected by changes in eggshell permeability and by intrinsic and extrinsic enzymes.
Helminth infections can cause pulmonary pathology due to larval migration through the lung vasculature or through the lung tissue causing a diffuse lung disease. Intermediate host Eukaryotic flagella differ from prokaryotic flagella because only eukaryotic flagella Contain microtubules. The plerocercoid larva develops into an adult worm in the definitive final host.
Activities of fungi that are considered detrimental from a human perspective. Helminths life cycle D. In humans helminths generally infect the a.
Helminths are transmitted to humans in many different ways. Biology questions and answers. Additionally trapped larvae or eggs can cause focal lesions within the lungs.
1 skin penetration OR ingestion of animal flesh secondary host 2 goes to organs such as intestine or bladder circulation 3 eggs develop into. Sometimes infective larvae of parasites are reported in accidental hosts which do not occur in the food chain of the definitive host. Within the host Enterobius and Trichuris mature directly in the intestine after a brief penetration in the mucosa.
Asked Aug 7 2019 in. The deposition of helminth eggs in feces is the starting point for the contamination of the pasture and the subsequent development of the parasites. Larval development of Helminths occurs in which host.
The coracidium develops into a procercoid stage in its micro-crustacean first immediate host and then into a plerocercoid larva in its next intermediate host which is a vertebrate. PDF Neglected tropical diseases caused by metazoan parasites are major public health concerns and therefore new methods for their control and. A form of host-induced arrest occurs in the paratenic host host factors eliciting a developmental response in the parasite that results in cessation of development and induction of diapause.
The larval stages of insects may be vulnerable to attack by diverse natural enemies including insect parasitoids that lay eggs on or in the vulnerable larva. In humans Helminths generally infect the. Human infection takes place by penetration of the larvae through skin.
Asked Apr 11 2021 in. Development is influenced by the same climatic factors as are hook worm larvae. Canis again provides an example of this form of developmental plasticity where rodents act as paratenic hosts Sprent 1958.
Assessment Saved Help During the life cycle of a parasitic helminth development of larvae occurs in the host while mating between adults occurs into 6 host. 3 cyst releases larva into the intestine -- replication. Larval development of helminths occurs in which host.
88 Larval development of helminths occurs in which host. Multiple Choice intermediate transport transport definitive intermediate definitive transport intermediate definitive transport.

The Chinese Liver Fluke Clonorchis Sinensis Is A Species Of Parasitic Worm That Is Classified Within The Digenea Ph Liver Fluke Parasitic Worms Invertebrates
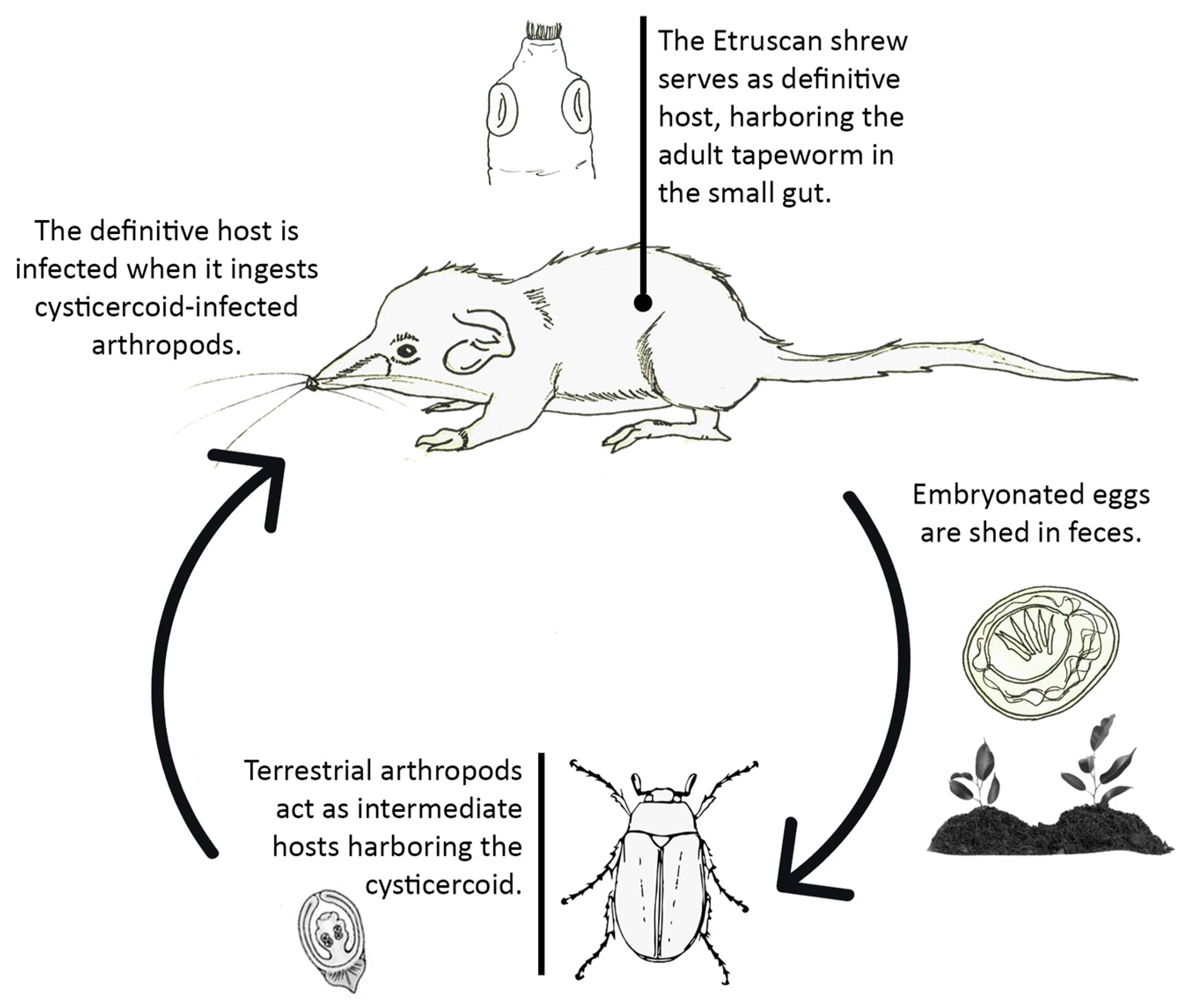
Animals Free Full Text First Data On The Helminth Community Of The Smallest Living Mammal On Earth The Etruscan Pygmy Shrew Suncus Etruscus Savi 1822 Eulipotyphla Soricidae Html

African Trypanosomiasis Biology Tsetse Fly Biology Life Cycles

Mechanisms Of Ev Involved In Host Parasite Interactions The Diagram Download Scientific Diagram
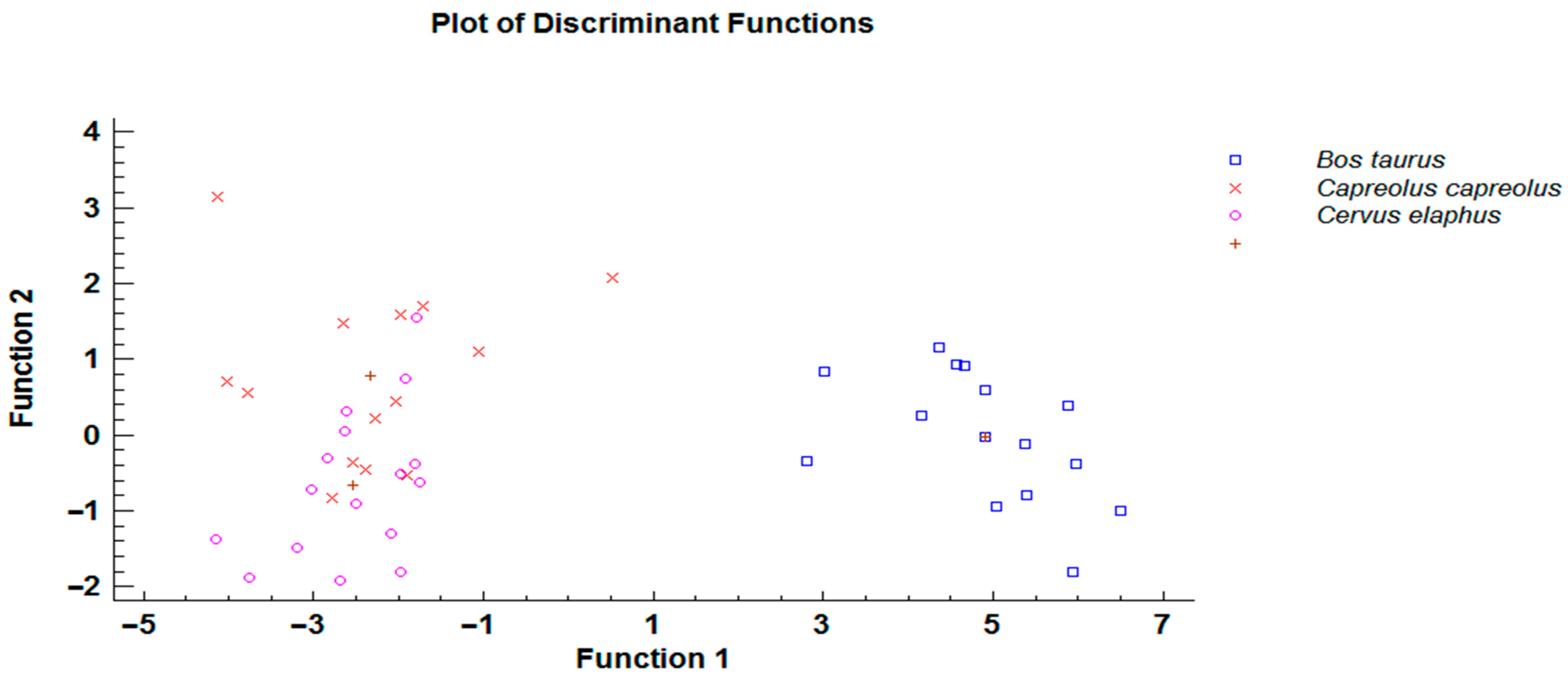
Animals Free Full Text Morphometric And Molecular Analyses Of Ostertagia Leptospicularis Assadov 1953 From Ruminants Species Diversity Or Host Influence Html

Possible Interactions Of Helminth Parasites With Host Mucins Download Scientific Diagram

The Ecology Of Parasites With Complex Life Cycles In Multi Host Systems Echinococcus Multilocularis Transmission Dynamics At Multiple Spatial Scales Alessandro Massolo 2 Updates Research Project
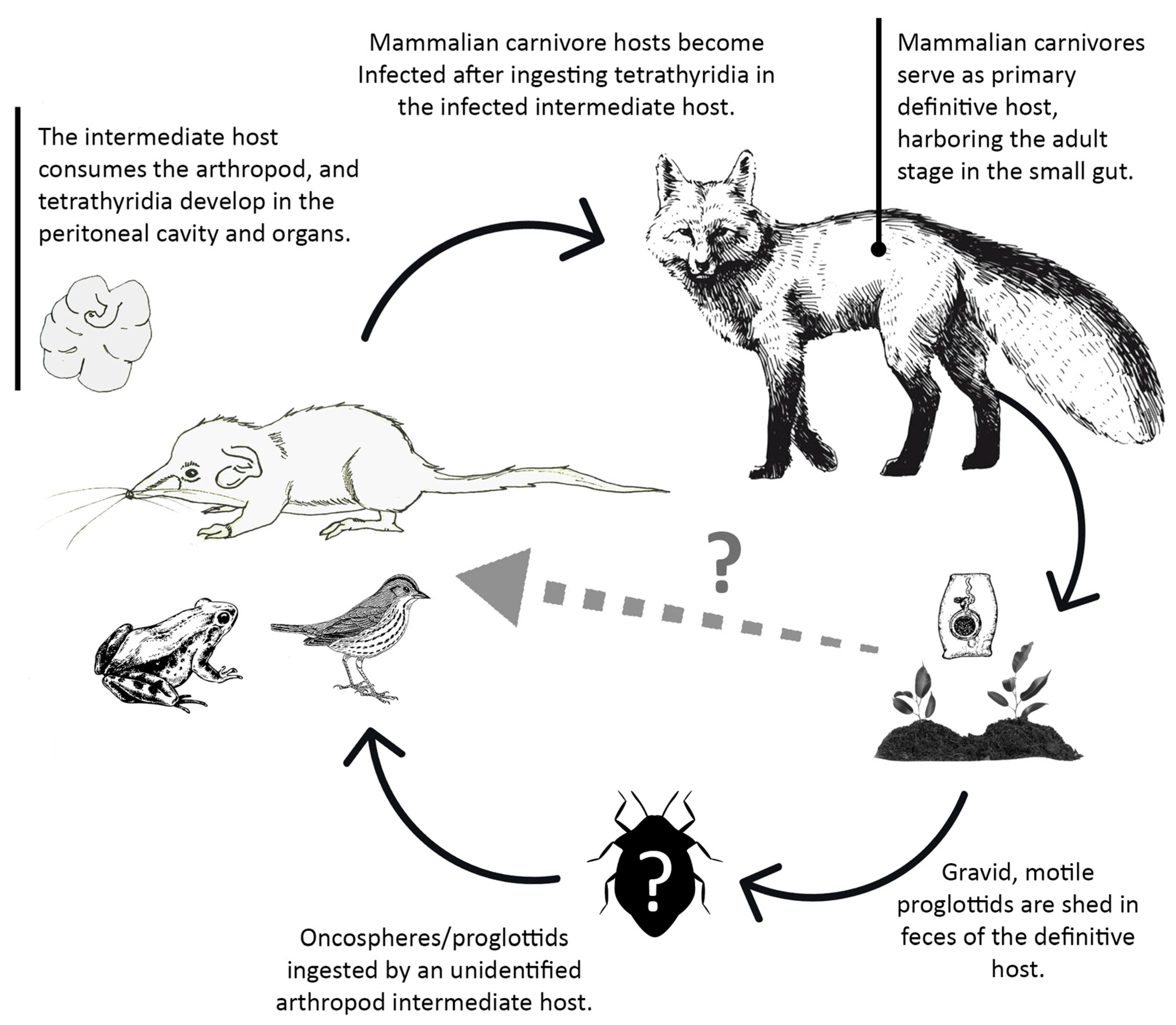
Animals Free Full Text First Data On The Helminth Community Of The Smallest Living Mammal On Earth The Etruscan Pygmy Shrew Suncus Etruscus Savi 1822 Eulipotyphla Soricidae Html

Ancylostoma Duodenale And Necator Americanus Lifecycle Parasite Life Cycles Intestinal Parasites
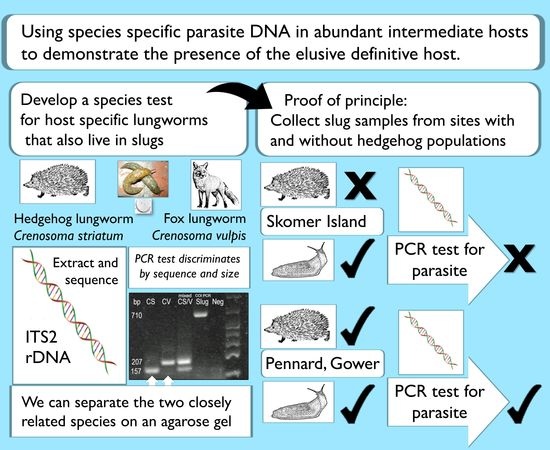
Animals Free Full Text Dna Footprints Using Parasites To Detect Elusive Animals Proof Of Principle In Hedgehogs Html
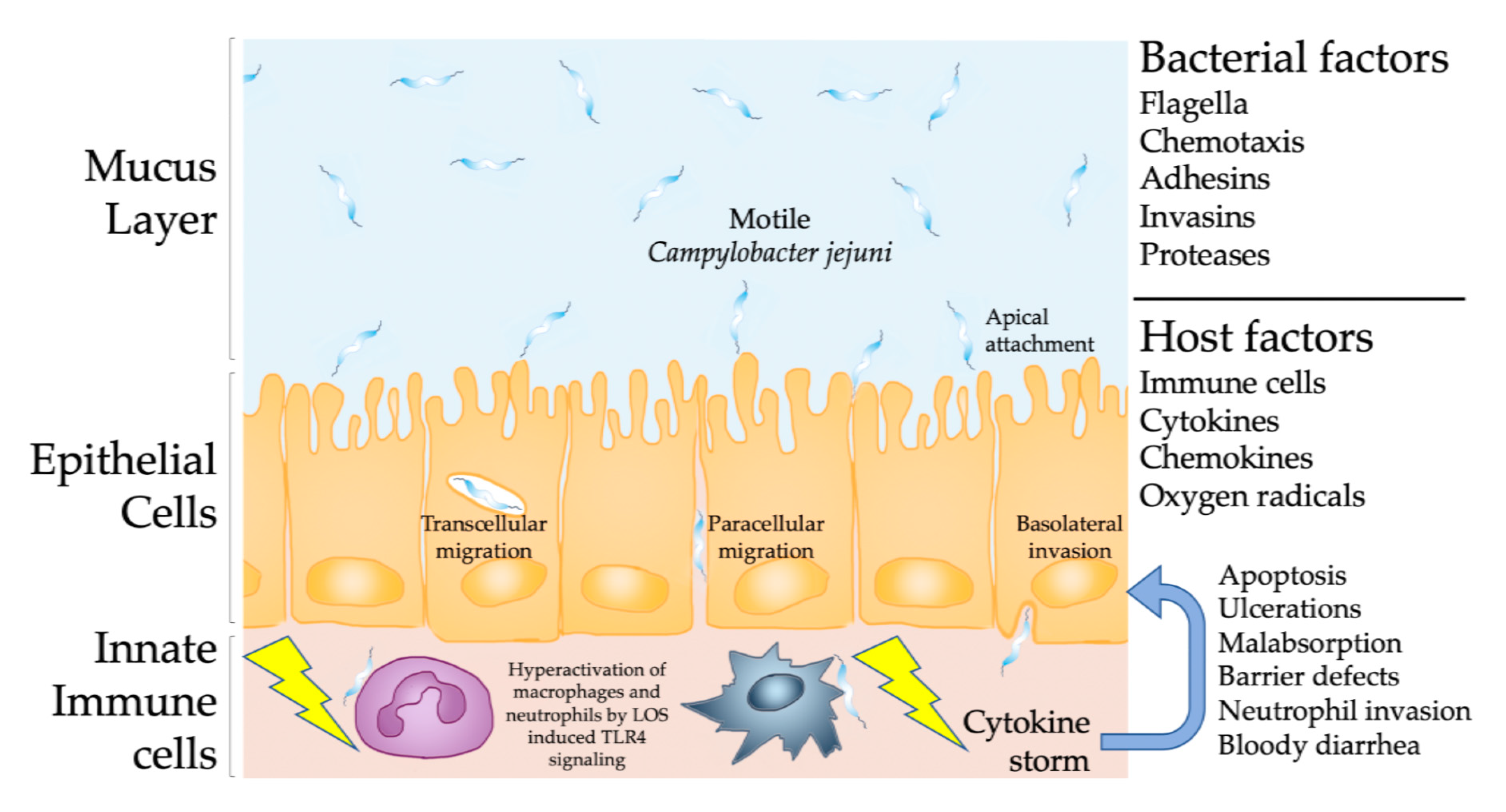
Microorganisms Free Full Text Novel Clinical Campylobacter Jejuni Infection Models Based On Sensitization Of Mice To Lipooligosaccharide A Major Bacterial Factor Triggering Innate Immune Responses In Human Campylobacteriosis Html

Helminthic Infections Oncohema Key
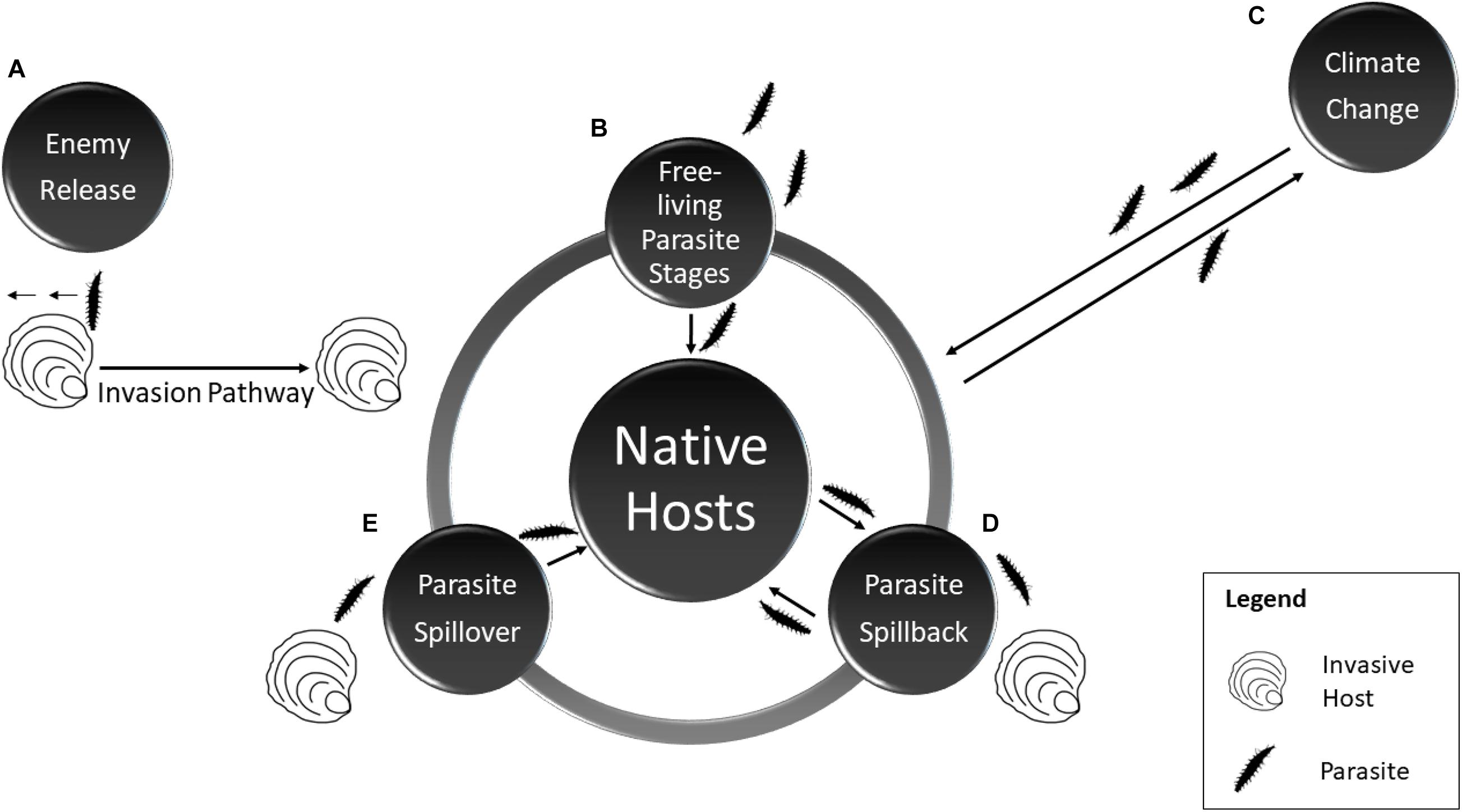
Frontiers The Importance Of Marine Bivalves In Invasive Host Parasite Introductions Marine Science
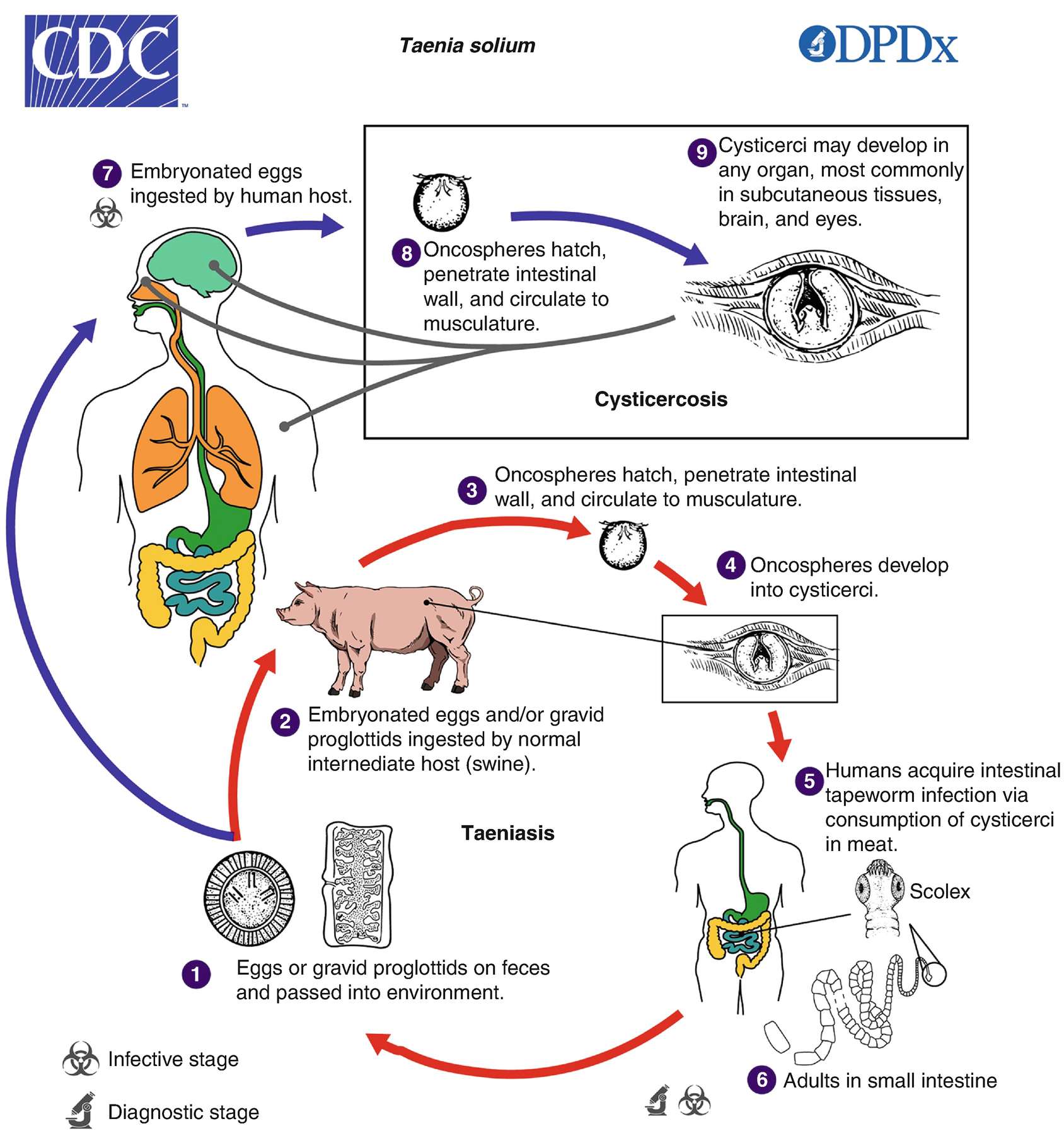
Human Helminth Infections A Primer Springerlink
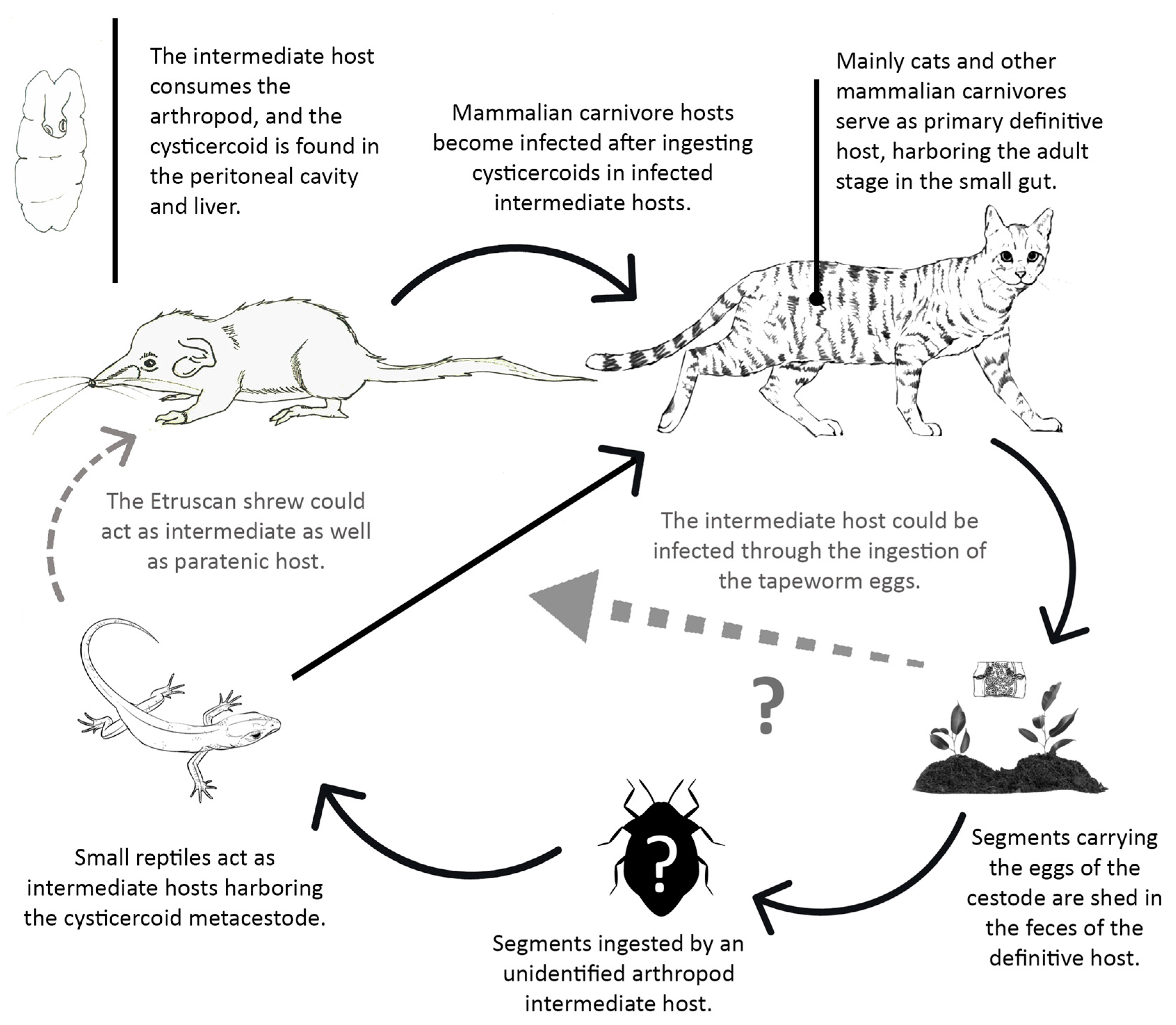
Animals Free Full Text First Data On The Helminth Community Of The Smallest Living Mammal On Earth The Etruscan Pygmy Shrew Suncus Etruscus Savi 1822 Eulipotyphla Soricidae Html

Typical Furcocercous Type Forked Tail Cercaria Of The Family Schistosomatidae The Cercaria Of Schistosome Rectangle Glass Contaminated Water Better Living

Pdf Life Cycle Complexity In Helminths What Are The Benefits
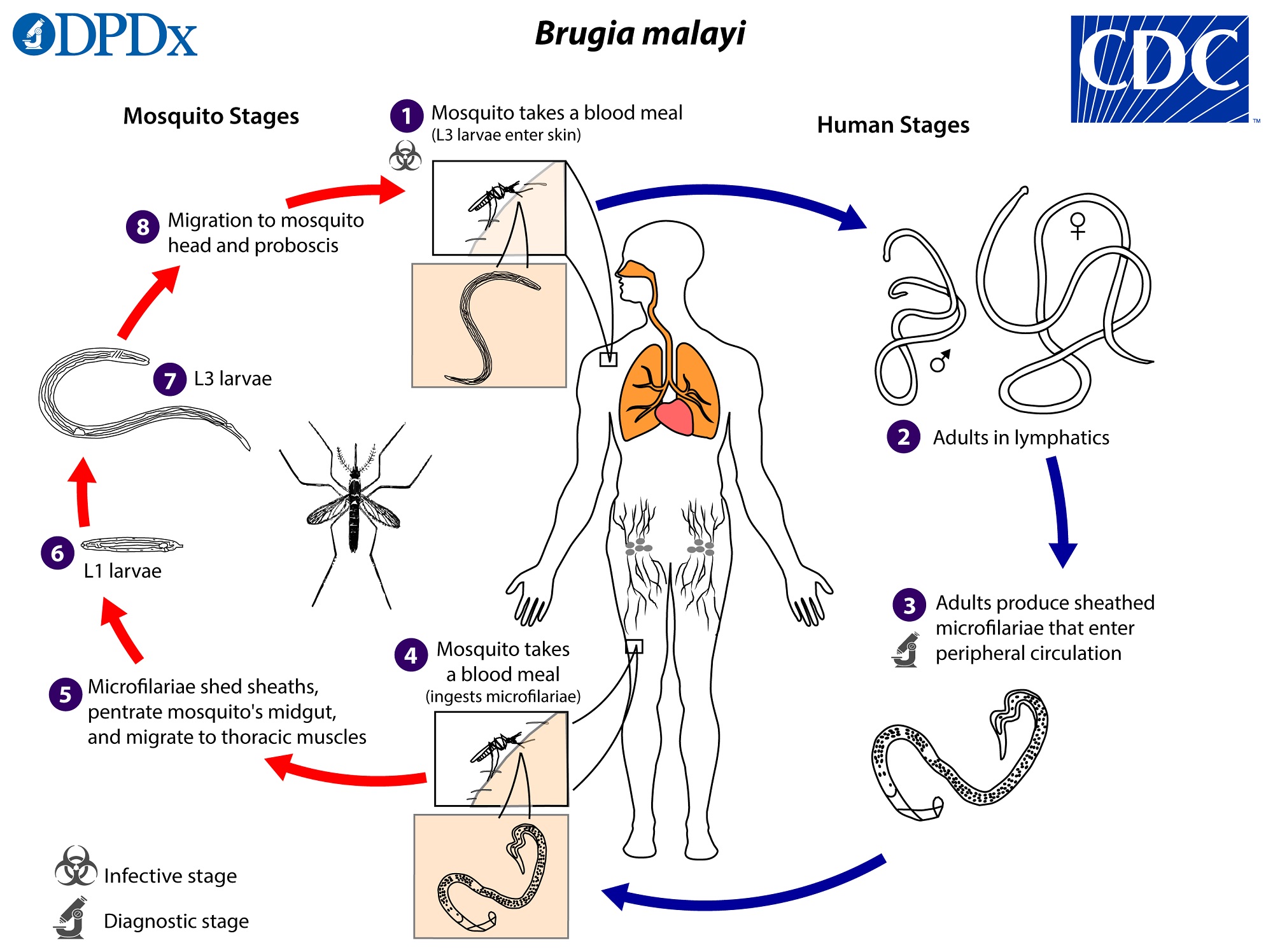

Comments
Post a Comment